Understanding Weather Storms and Tornadoes: An Overview

Introduction
Weather storms and tornadoes are significant natural phenomena that capture the attention of meteorologists and the public alike. They can cause extensive damage and disrupt communities, making understanding their formation, patterns, and impact vital for preparedness and response efforts. In Canada, where storm activities are common, especially during the spring and summer months, awareness of these weather patterns is crucial.
The Science Behind Weather Storms
Weather storms can manifest in various forms, including thunderstorms, snowstorms, and gusty winds, driven by various meteorological factors. A thunderstorm, characterized by lightning, heavy rain, and strong winds, develops due to the confluence of warm, moist air rising and cooler, denser air sinking. These conditions lead to instability in the atmosphere, which can escalate into more severe weather types.
Tornado Formation
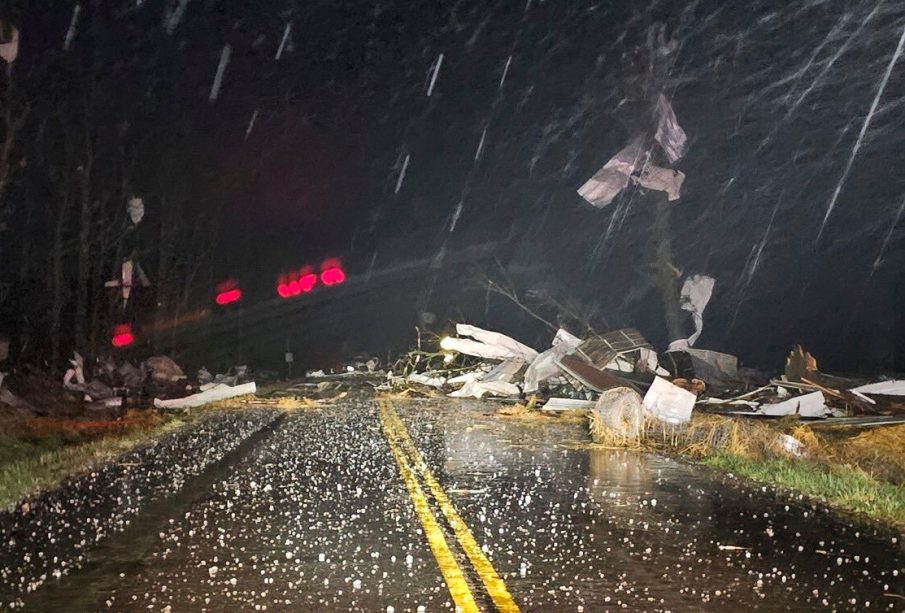
Tornadoes are one of the most destructive types of weather storms, forming from severe thunderstorms, particularly supercells. A tornado occurs when a rotating column of air develops between a thunderstorm and the ground. Canada is not immune to these storms, as the country experiences around 40 tornadoes annually, with the Prairie Provinces often taking the brunt of these natural disasters.
Recent Tornado Events in Canada
In July 2023, southern Ontario and Quebec faced a series of tornadoes that caused significant damage across communities. The storm system resulted in widespread power outages and property damage, highlighting the need for effective emergency preparedness. According to Environment and Climate Change Canada, both provinces reported multiple tornado sightings, leading to upgraded warnings and an increased focus on public safety.
Preparedness and Response
Understanding the signs of severe storms and potential tornadoes is key to minimizing risk. Both Environment Canada and local authorities provide resources and alerts to educate the public on how to react when hazardous conditions are predicted. The enhancement of technology in weather prediction has improved advance warnings, allowing communities to respond more effectively than in previous years.
Conclusion
Weather storms and tornadoes remain topics of critical importance due to their potential implications on safety, property, and the environment. Ongoing education and increasing awareness can help communities mitigate risk and better prepare for these unpredictable forces of nature. With climate change continuing to influence weather patterns, understanding these phenomena will be paramount for future safety measures and disaster response strategies in Canada.