Understanding the Meaning of Recession
Introduction
In the current economic landscape, the term “recession” has become increasingly prevalent as experts and policymakers navigate through various economic challenges. A recession refers to a significant decline in economic activity that lasts for an extended period, typically visible in real GDP, income, employment, manufacturing, and retail sales. Understanding the meaning of recession is crucial for businesses, consumers, and investors, as it can significantly impact financial decisions and strategies.
What is a Recession?
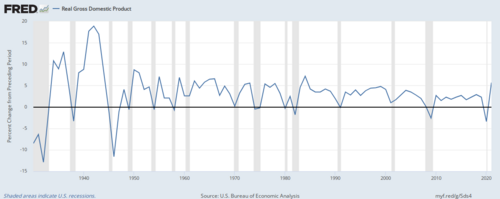
A recession is generally defined as two consecutive quarters of negative growth in a country’s gross domestic product (GDP). It indicates that the economy is contracting rather than expanding, leading to widespread implications for employment rates and consumer spending. Various factors can trigger a recession, including high inflation, increased interest rates, reduced consumer confidence, and external shocks such as pandemics or global economic fluctuations.
Recent Events and Economic Indicators
In Canada, recent events have raised concerns about the possibility of a recession, particularly in light of rising interest rates set by the Bank of Canada to combat inflation. As borrowing costs climb, businesses and consumers may curtail spending, leading to slower economic growth. According to Statistics Canada, GDP growth slowed to 1.6% in the last quarter, down from previous periods, prompting analysts to closely monitor the economic situation. Furthermore, economists predict that certain sectors, such as housing and retail, might feel the brunt of a downturn as consumer confidence wanes.
Impacts of a Recession
The impact of a recession can be severe. Job losses may mount as companies look to cut costs, and unemployment rates could rise significantly, leading to decreased consumer spending. Additionally, the stock market often reacts negatively to recessionary signals, resulting in lower investment values. This cycle can create a snowball effect, as reduced spending leads to further contractions in economic growth. In response, governments may implement measures such as stimulus packages or tax cuts to promote economic stability and recovery.
Conclusion
Understanding the meaning of recession and its potential impacts is essential for navigating the current economic landscape. As businesses and consumers brace for possible economic slowdowns, remaining informed about economic indicators and trends can help mitigate risks. While recessions can present challenges, they also provide opportunities for recovery and growth in the long term. It is crucial for stakeholders to stay vigilant and adaptable to ensure resilience in their financial strategies during these uncertain times.