Understanding the Canada Inflation Rate in 2023
Introduction
The inflation rate in Canada has become a critical topic of discussion amidst ongoing economic challenges. As of 2023, inflationary pressures have significantly impacted consumers and businesses alike. Understanding the causes and effects of changes in the inflation rate is crucial for Canadians to navigate financial decisions and policies effectively.
Current State of Inflation in Canada
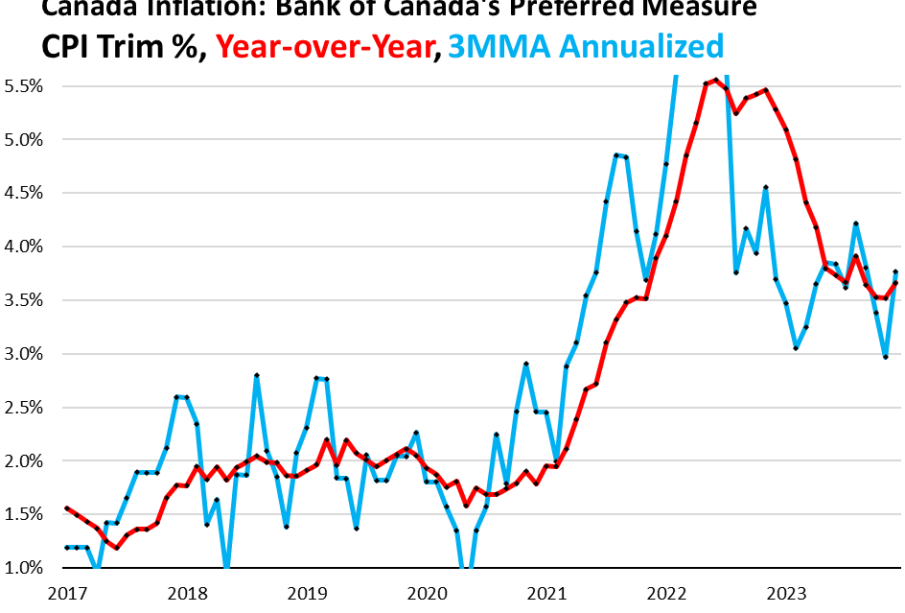
Recent data from Statistics Canada indicates that the inflation rate has stabilized at approximately 6.4% annually as of September 2023, a noticeable decrease from the peak above 8% recorded in June of the previous year. This reduction reflects the Bank of Canada’s ongoing efforts to curb inflation through interest rate hikes and monetary policy adjustments.
Key factors contributing to current inflation include rising energy prices, supply chain disruptions, and increased consumer demand post-pandemic. For instance, energy prices have surged by 8.8% year over year, primarily due to geopolitical tensions and fluctuating global markets. Similarly, costs for groceries have risen significantly, affecting household budgets across the nation.
Economic Impact
The inflation rate has wide-ranging implications for the Canadian economy. High inflation diminishes purchasing power, making everyday goods and services more expensive for consumers. This has led to concerns among Canadians, with many reporting difficulty in managing existing financial commitments, such as mortgages and rents.
Businesses are also feeling the strain as input costs rise, prompting many to either increase prices or absorb costs, which could affect profit margins and employment levels. Furthermore, sectors such as hospitality and retail are particularly vulnerable as consumer spending habits shift in response to inflationary pressures.
Future Projections and Considerations
Looking forward, experts predict that the Canada inflation rate may hover around the 4-5% mark into early 2024 before gradually declining as monetary policy takes effect. The Bank of Canada remains committed to controlling inflation to restore price stability, but global economic pressures could complicate these efforts.
For Canadians, it is essential to remain informed about inflation trends and their implications. As inflation continues to evolve, consumers may need to adapt to changing economic conditions, which could include adjusting budgets and spending habits.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the current inflation rate in Canada has heightened awareness around economic management for both individuals and businesses. With sound monetary policy and proactive measures, there is hope for stabilization in the future; however, ongoing vigilance is necessary as the landscape continues to change. Understanding the intricacies of the inflation rate is essential for consumers to make informed decisions in an evolving economic environment.









