Understanding the Bird Flu Outbreak in Canada 2023

Introduction to Bird Flu
The avian influenza, commonly known as bird flu, has re-emerged as a significant public health concern in Canada. With an increase in reported cases over the last few months, the impact of this outbreak extends beyond wildlife health to agriculture, animal husbandry, and even human health risks. Understanding the dynamics of bird flu is essential for mitigating its effects and protecting food sources.
Current Situation in Canada
Recent reports from the Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) indicate a rise in confirmed cases of bird flu across multiple provinces, including Ontario and Quebec. In these regions, both wild and domesticated birds have been affected. The virus, primarily H5N1, poses a serious threat to poultry farms, resulting in culling and biosecurity measures aimed at containing the outbreak.
In September 2023, the CFIA confirmed that over 1.5 million birds had been euthanized since the start of the outbreak. Many farms have instituted enhanced biosecurity protocols, including restrictions on the movement of birds and strict sanitation practices to prevent further transmission of the virus.
Public Health Concerns
While bird flu is primarily a disease that affects birds, experts caution that strains such as H5N1 can potentially infect humans, especially those in close contact with infected poultry. The World Health Organization (WHO) has stated that while the risk to the general public remains low, vigilance is necessary. Reports from previous outbreaks worldwide indicate that the virus can cause serious illness in humans, leading to hospitalizations and fatalities.
Impact on the Agricultural Sector
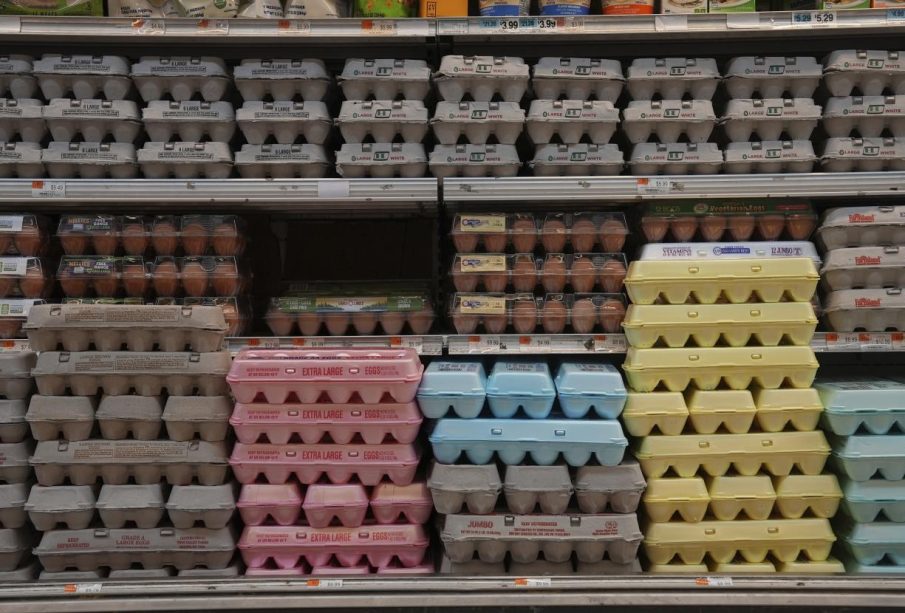
The agricultural sector is feeling the pressure from this outbreak. Farmers are facing economic losses due to the culling of large poultry populations and the costs associated with heightened biosecurity measures. Additionally, consumers may experience rising prices for eggs and poultry products as supply decreases, potentially leading to food security concerns.
Conclusion
The ongoing bird flu outbreak in Canada is a multifaceted issue affecting wildlife, agriculture, and public health. As authorities work to contain the spread of the virus, it is imperative for the farming community, policymakers, and the general public to stay informed and prepared. Continued research into vaccines and treatments is crucial in preventing future outbreaks and protecting both animal and human populations. For consumers, being aware of the situation can help in making informed purchasing decisions regarding poultry products during this challenging time.