Understanding EU Tariffs and Their Economic Impact
Introduction to EU Tariffs
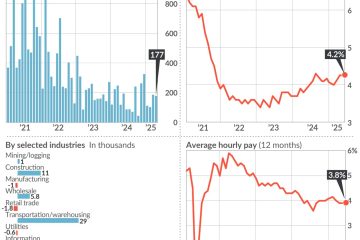
European Union tariffs play a crucial role in shaping international trade dynamics and economic relations. These tariffs, or taxes imposed on imported goods, have far-reaching implications for businesses, consumers, and government policies within the EU member states. As the global economy continues to evolve, the impact of these tariffs has become increasingly relevant, particularly in the context of ongoing trade negotiations, geopolitical tensions, and economic recovery efforts following the COVID-19 pandemic.
Current Events Surrounding EU Tariffs
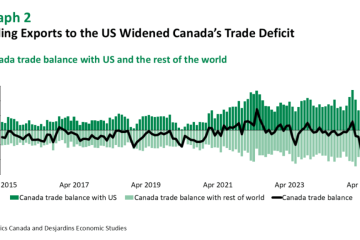
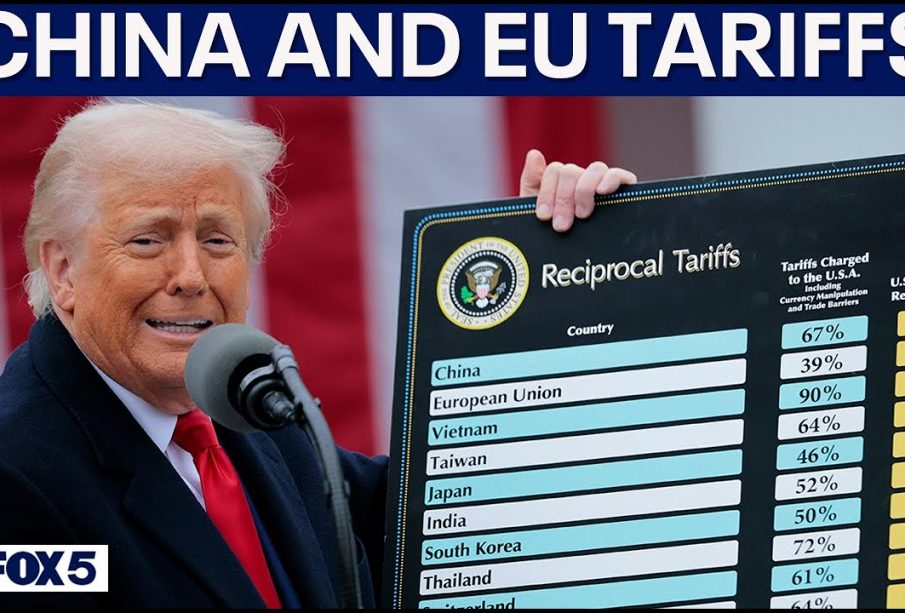
In recent months, the EU has faced significant trade challenges, particularly in its dealings with major partners such as the United States and China. The introduction of tariffs on various imported goods has been a key strategy employed to protect local industries and generate revenue. For example, in early 2023, the EU imposed tariffs on certain electronics and agricultural products from the US in response to what it considered unfair trade practices. This decision sparked a heated debate over the long-term implications for transatlantic relations.
Moreover, the EU’s tariffs on Chinese goods, particularly in the technology sector, are aimed at countering practices such as dumping and intellectual property theft. In September 2023, the European Commission proposed new tariffs on solar panels manufactured in China, asserting the need for fair competition and sustainable practices. This move highlights the EU’s commitment to balancing market protection with its climate goals, reflecting a broader trend in global trade policy.
Economic Implications of EU Tariffs
The impact of EU tariffs extends beyond trade balances, influencing economic growth, inflation rates, and consumer behavior within the union. High tariffs can lead to increased prices for imported goods, ultimately affecting consumers who may face limited options and higher costs. Economists project that sustained high tariffs could contribute to rising inflation within the EU, complicating recovery efforts in the post-pandemic economy.
Conversely, proponents of tariffs argue that they support local industries, fostering job creation and economic stability. By protecting home-grown businesses from foreign competition, the EU aims to bolster its economic resilience in an ever-competitive global landscape. However, the risk of trade retaliation looms, as affected nations may impose their own tariffs, leading to a cycle of escalation that could ultimately harm all parties involved.
Conclusion and Future Outlook
The significance of EU tariffs in the current global economy cannot be understated. As trade relationships continue to evolve in light of economic recovery and geopolitical factors, it is crucial for policymakers and businesses to navigate these challenges thoughtfully. Looking ahead, the EU may need to balance protectionist measures with the benefits of free trade, as it strives to maintain its position in the global marketplace. Analysts predict that the EU’s tariff policies will remain a focal point in international negotiations, with an emphasis on finding a balance between protecting local interests and fostering global trade partnerships.