Understanding Climate Tipping Points and Their Impact
Introduction
Climate tipping points are critical thresholds in the Earth’s climate system that, when crossed, can lead to significant and potentially irreversible changes in the ecosystem. These points have garnered increased attention among scientists and policymakers as the planet experiences escalating temperatures, rising sea levels, and extreme weather events. Recognizing and understanding these tipping points is essential for developing effective strategies to mitigate climate change and protect our environment for future generations.
What Are Climate Tipping Points?
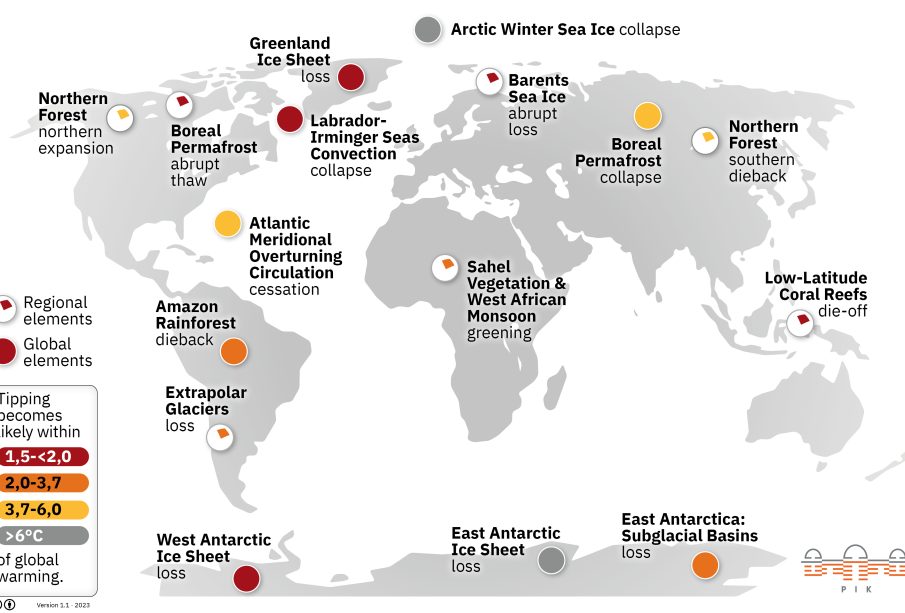
Tipping points refer to thresholds beyond which a small change can lead to drastic and irreversible effects on the environment and climate. Examples include the melting of the Greenland ice sheet, the dieback of the Amazon rainforest, and the thawing of permafrost in Arctic regions. These events can unleash feedback loops, exacerbating climate change and leading to even more severe consequences.
Recent Developments and Findings
Recent research has highlighted alarming trends associated with climate tipping points. A study published in ‘Nature Climate Change’ reports that as many as five major tipping points could be reached before the global temperature rise surpasses 2°C above pre-industrial levels. This could trigger widespread disruptions not only in local ecosystems but also in global weather patterns, agriculture, and food security.
In August 2023, scientists discovered unprecedented melting of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet, indicating that we may already be at risk of crossing tipping points sooner than previously anticipated. The rapid decline of ice in this region is a stark reminder of the urgent need for comprehensive climate action.
The Importance of Addressing Tipping Points
Understanding and addressing climate tipping points is not merely an academic pursuit; it has profound implications for global efforts to combat climate change. By recognizing the risks associated with these thresholds, countries can prioritize resilience measures, emission reductions, and sustainable development practices.
Conclusion
In summary, climate tipping points represent a critical challenge in our fight against climate change. As scientific evidence mounts indicating the proximity of these thresholds, there is an urgent need for collective global action. Policymakers, businesses, and individuals must work together to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and implement sustainable practices to minimize the risk of triggering irreversible impacts. Failing to act could result in severe consequences for biodiversity and human societies, making it imperative that we heed the warning signs and strive for meaningful change.







