Understanding Chronic Venous Insufficiency: Causes and Treatments
Introduction to Chronic Venous Insufficiency
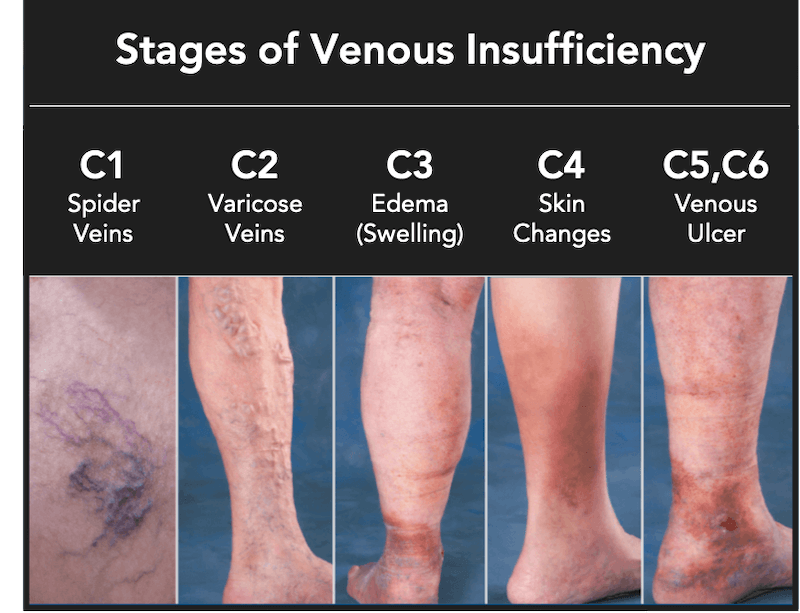
Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) is a common medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. This disorder occurs when veins in the legs struggle to send blood back to the heart effectively, leading to a host of uncomfortable symptoms. Understanding CVI is essential not only for those who are affected but also for healthcare professionals who provide care. With an aging population and changing lifestyle factors, chronic venous insufficiency is increasingly relevant in today’s healthcare landscape.
What Causes Chronic Venous Insufficiency?
Several factors contribute to the development of chronic venous insufficiency. The most common cause is weakened valve function within the veins. These valves usually ensure that blood flows in one direction, but when they fail, blood can pool in the veins, leading to increased venous pressure. Risk factors for CVI include:
- Age: Older adults are at higher risk due to degeneration of vein function.
- Genetics: Family history of venous problems can predispose individuals to CVI.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts additional pressure on the veins.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and increased blood volume can affect vein health.
- Prolonged Standing or Sitting: Jobs that require long periods of immobility can exacerbate venous issues.
Symptoms of Chronic Venous Insufficiency
Patients suffering from CVI often experience a variety of symptoms that can impact their quality of life. Key symptoms include:
- Swelling in the legs or ankles
- Pain or heaviness in the legs, especially after prolonged standing
- Itching or inflammation
- Varicose veins
- Skin changes, such as discoloration or ulcers
Treatment Options for Chronic Venous Insufficiency
Management of chronic venous insufficiency typically focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing complications. Treatment options include:
- Compression Therapy: Wearing compression stockings can help improve blood flow in the legs.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Weight management, exercise, and leg elevation can reduce symptoms.
- Medications: In some cases, medications may be prescribed to improve circulation.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: Options such as endovenous laser therapy or sclerotherapy can treat varicose veins and improve outcomes.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical interventions may be required to address underlying vein problems.
Conclusion: The Future of Chronic Venous Insufficiency Care
As awareness grows regarding the implications of chronic venous insufficiency, healthcare providers are better equipped to offer effective treatments and support. Ongoing research is essential to improve understanding of CVI and develop innovative therapies. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of chronic venous insufficiency, seeking medical advice can lead to improved health outcomes and a better quality of life. With the right care, many people with CVI can manage their symptoms effectively and continue to lead active lives.









