Understanding Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease and Its Implications
Introduction
Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease is an inherited neurological disorder that affects the peripheral nerves, leading to muscle weakness and atrophy. Recognizing its significance is crucial for patients, families, and healthcare providers as it not only impacts quality of life but also has severe implications, including potentially premature death. As awareness of CMT increases, it is essential to shed light on its progression and the complexities associated with the disease.
The Nature of Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease
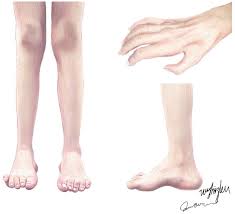
CMT encompasses a group of inherited disorders, primarily characterized by the degeneration of peripheral nerves. Caused by genetic mutations, CMT affects approximately 1 in 2,500 individuals in the United States and is one of the most common inherited neuropathies. Symptoms usually manifest in adolescence or early adulthood but can vary significantly in severity and type. Common symptoms include muscle weakness, atrophy, and sensory loss, particularly in the feet and hands.
Factors Related to Disease Progression and Outcomes
While CMT itself is not defined as a fatal disease, it can lead to severe complications that might increase mortality risk. Factors such as the type of CMT, age of onset, and overall health contribute to the disease’s progression. Some patients may experience significant functional impairment, which can lead to secondary complications such as falls, loss of mobility, and respiratory difficulties, which can be life-threatening. Recent studies indicate that individuals with advanced stages of CMT may have an increased risk of mortality compared to the general population, largely due to the complications arising from the disease.
Current Research and Outlook
Researchers are actively studying CMT to improve diagnostic measures and identify targeted therapies. Advances in genetic testing can now classify specific subtypes of the disease, allowing for personalized care plans. These developments are crucial as they enhance the understanding of CMT’s impact and provide hope for potential treatments. While there is currently no cure for CMT, innovative research may lead to better management strategies and improved quality of life for those affected.
Conclusion
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease significantly impacts many lives, affecting mobility and health and sometimes leading to severe outcomes, including premature death. Awareness, education, and ongoing research are paramount to improving care and support for individuals with CMT. As scientists strive to unlock the mysteries of this complex disease, there is hope that with advancements, we can mitigate its effects and enhance the longevity and quality of life for those affected by Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease.