Understanding Bank of Canada Interest Rate Decisions
Introduction
The Bank of Canada’s interest rate decisions are pivotal in shaping the country’s economic landscape. As the central bank of Canada, it regulates monetary policy to maintain price stability and foster economic growth. Recent trends and adjustments in the interest rates have spurred conversations among economists, businesses, and consumers about the potential implications for borrowing, spending, and savings.
Current Interest Rate Trends
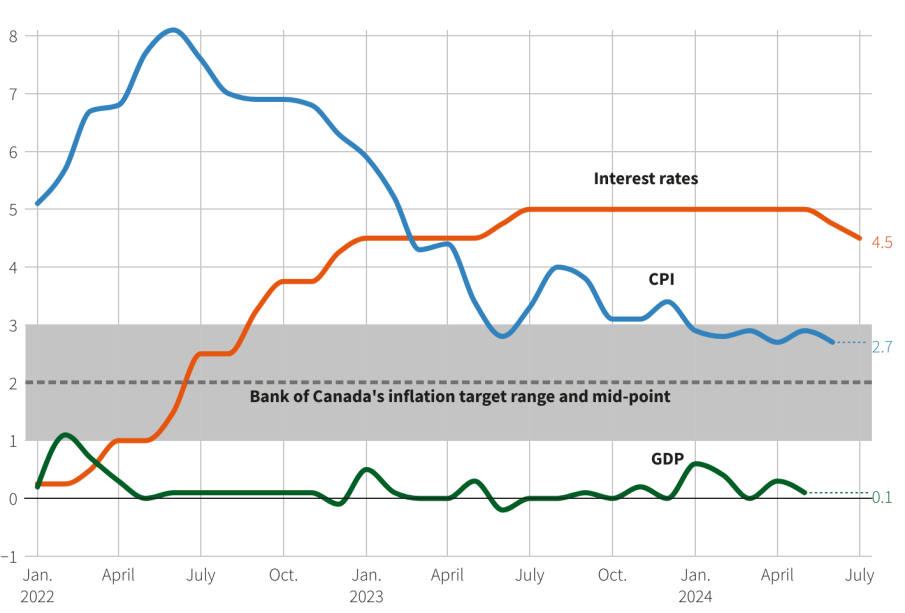
As of October 2023, the Bank of Canada has sustained its benchmark interest rate at 5.00%, a level maintained since July following several hikes throughout the past year. These decisions stem from ongoing inflationary pressures caused by both global economic conditions and domestic factors. The rate increase strategy implemented over the past year aimed to combat inflation, which peaked at 8.1% in June 2022.
Impact on the Economy
The maintenance of the current interest rate has led to varied responses across different sectors of the economy. For consumers, higher interest rates generally result in increased costs of borrowing for mortgages, credit cards, and loans, making it less attractive to engage in large purchases. Conversely, the higher rates benefit savers who may earn more interest on their savings accounts and fixed-income investments.
Businesses also feel the strain of higher borrowing costs, as they may reduce expansion plans or delay investment due to uncertainty surrounding consumer spending. However, the governor of the Bank of Canada, Tiff Macklem, has indicated that the central bank remains vigilant and will make adjustments as needed to ensure economic stability.
Future Projections
Looking ahead, analysts suggest that the Bank of Canada may consider further interest rate adjustments depending on upcoming economic indicators such as inflation rates, unemployment levels, and overall economic growth performance. Forecasts indicate a possibility that the central bank may lower rates by the end of 2024 if inflation trends downward towards the target of 2%.
Conclusion
The Bank of Canada’s interest rate policies are crucial for shaping both short-term economic conditions and long-term financial trends in Canada. For readers, keeping an eye on these developments will be important for personal finance decisions, whether it involves mortgages, investments, or savings strategies. As rates evolve, consumers and businesses alike must remain adaptable to the shifting economic landscape.







