Understanding 23andMe: The Future of DNA Testing
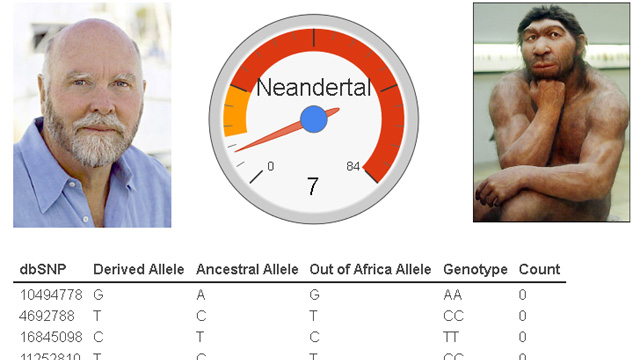
Introduction to 23andMe
In a world increasingly driven by technology and personalized medicine, consumer genetic testing has become a valuable tool for those seeking to learn more about their ancestry and health. 23andMe, a pioneer in the field of direct-to-consumer DNA testing, has risen to prominence since its inception in 2006. Its importance lies not only in its ability to provide insights into a person’s genetic makeup but also in its contribution to advancing the understanding of genetics at large.
What is 23andMe?
Founded by Anne Wojcicki, Linda Avey, and Paul Cusenza, 23andMe offers a service that allows individuals to discover their genetic background, potential health risks, and traits by analyzing their DNA. Customers simply order a kit, provide a saliva sample, and send it back to the laboratory for testing. Within a few weeks, they receive a comprehensive report detailing their ancestry composition, health predispositions, and even traits they may possess.
Recent Developments
In recent months, 23andMe has made headlines for its ongoing efforts to innovate and enhance its services. The company has added new features to provide more personalized health insights, including reports on wellness traits such as sleep quality and lactose intolerance. Additionally, 23andMe has collaborated with pharmaceutical companies to utilize genetic data for drug development, strengthening the connection between genetics and healthcare.
The COVID-19 pandemic also influenced 23andMe’s direction, prompting the company to investigate genetic factors related to immune responses. As a result, they launched a new initiative focused on studying the genetic variables affecting the severity of COVID-19 infections. This move positions 23andMe at the forefront of genetic research during a critical time.
Ethical Considerations
As with any technology that involves the handling of sensitive personal data, ethical considerations are paramount. 23andMe has encountered scrutiny regarding data privacy and user consent. The company assures users that their genetic data is protected and that it is only shared with third parties when consent is granted. Transparency in how genetic data is collected and utilized remains a topic of ongoing discussion in the industry.
Conclusion: The Future of Genetic Testing
As the popularity of services like 23andMe continues to grow, the implications for health and ancestry research are considerable. These insights can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health and lifestyle, while also contributing to broader genetic research initiatives. Moving forward, it will be crucial for 23andMe and similar companies to maintain ethical standards and prioritize consumer privacy as they navigate the complex landscape of genetic testing. For consumers, the importance of understanding the intricacies and implications of their genetic data cannot be overstated; it may pave the way for personalized healthcare in the future.








