The Impact of the Bank of Canada Interest Rate on the Economy
Introduction
The Bank of Canada (BoC) plays a vital role in shaping the economic landscape of Canada through its interest rate decisions. The interest rate set by the BoC influences borrowing costs, consumer spending, and overall economic growth. As of now, investors and consumers alike are watching closely to understand the potential implications of recent interest rate changes, especially in a post-pandemic economy.
Recent Developments
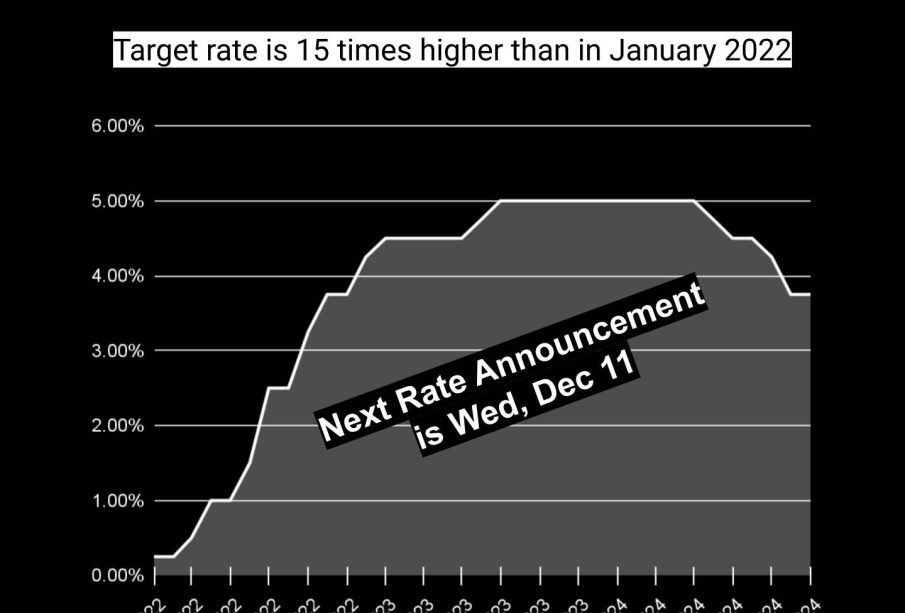
On October 25, 2023, the Bank of Canada announced a surprise increase in its key interest rate, raising it from 4.50% to 4.75%. This decision comes in response to persistent inflationary pressures, which have remained above the BoC’s target of 2%. The central bank is aiming to curb inflation by making borrowing more expensive and thereby reducing spending.
In the past few months, inflation rates have been driven by factors such as supply chain disruptions, higher energy prices, and the overall resilience of the labor market. As reported, Canada’s inflation rate has hovered around 4.1%, significantly above the acceptable range, prompting the BoC’s decisive action. Analysts forecast that if inflation continues to stay above target, further rate hikes might be on the table in the coming months.
Reactions and Repercussions
The recent interest rate hike has led to mixed reactions across various sectors. Homeowners with variable-rate mortgages are feeling the pinch as monthly payments rise. The real estate sector, already in a cooling phase, is likely to experience additional slowdowns as potential buyers reconsider their financial commitments.
On the other hand, higher interest rates can benefit savers and those with fixed-income securities as yields increase. Financial analysts suggest that this rate hike could also lead to a stronger Canadian dollar, which could be beneficial for imports but may negatively impact exporters as their goods become relatively more expensive abroad.
Conclusion
The Bank of Canada’s recent interest rate increase signifies its commitment to addressing enduring inflation while striving for economic stability. For Canadian consumers, the hike may pose challenges in terms of increased borrowing costs, but it also presents an opportunity for savers. As inflation rates remain a concern, the BoC’s future monetary policy decisions will be critical for shaping the economic environment in Canada. Stakeholders should continue to monitor developments closely to navigate the changing economic landscape effectively.








