The Impact of Tariffs on Global Trade and Economy

Introduction to Tariffs
Tariffs have become a crucial aspect of international trade, serving as both a tool for governments to protect domestic industries and a point of contention in global economic relations. As countries navigate trade negotiations and make decisions that affect their economies, understanding tariffs and their implications has never been more important.
What are Tariffs?
Tariffs are taxes imposed by governments on imported goods and services. They can be used to increase the cost of foreign products, making domestic products more competitive. Tariffs can take various forms, including specific tariffs, which charge a fixed amount per unit imported, or ad valorem tariffs, which charge a percentage of the value of the imported goods.
Recent Developments and Events
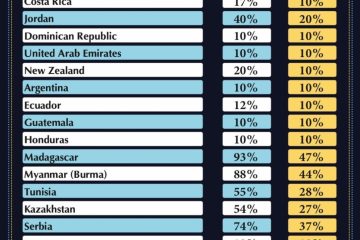
In recent years, tariffs have played a significant role in international trade policy, particularly between major economies such as the United States and China. In 2018, the U.S. implemented substantial tariffs on a variety of Chinese goods, prompting retaliatory measures from China. These actions escalated tensions and led to a series of negotiations aimed at resolving trade imbalances. As of October 2023, the ongoing discussions reflect a complex web of economic interests as both nations attempt to forge a path toward a more balanced trade relationship.
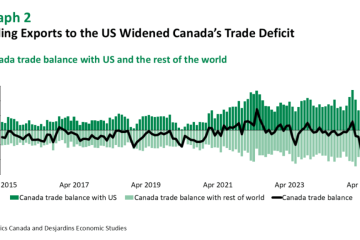
Moreover, the coronavirus pandemic has intensified debates around tariffs. Supply chain disruptions led governments to reconsider their reliance on foreign goods, resulting in calls for increased tariffs on imports considered essential. Countries like Canada are evaluating their approaches to tariffs in light of changing economic circumstances and are attempting to boost local production.
Effects of Tariffs on Economies
The impact of tariffs extends beyond the immediate financial implications. Economists warn that while tariffs may offer short-term benefits to specific sectors, they can lead to increased prices for consumers and strained relations with trade partners. For instance, sectors heavily reliant on imported materials, such as manufacturing and construction, may face higher costs that could ultimately affect consumers through increased prices.
Conclusion: The Future of Tariffs
As global trade continues to evolve, the significance of tariffs in shaping economic policies remains critical. With the potential for tariffs to both protect domestic industries and disrupt global trade networks, governments must carefully consider their approaches. Observers forecast that nations may continue to use tariffs strategically in future negotiations, balancing the need for market access with domestic economic interests. For businesses and consumers alike, staying informed about tariff policies will be essential to navigate the complexities of an ever-changing economic landscape.