The Impact of Chinese EV Tariffs on the Global Electric Vehicle Market
Introduction
In recent years, electric vehicles (EVs) have become a focal point of international trade, with Chinese manufacturers leading the charge in global production. However, recent developments in tariffs imposed by the Chinese government on imported EVs have raised concerns about the implications for global trade. Understanding these tariffs is crucial as they can significantly impact prices, supply chains, and the overall growth of the EV market.
The Tariff Landscape
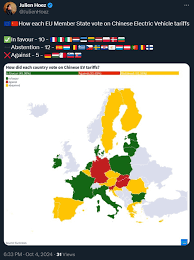
In early October 2023, the Chinese government announced a series of tariffs on imported electric vehicles and their components, citing the need to protect domestic manufacturers and foster local innovation. The tariffs, which can reach as high as 25%, are part of China’s broader strategy to bolster its own EV industry—an industry that has already captured a substantial market share worldwide.
This move comes at a time when the global push towards electric mobility is accelerating, driven by environmental regulations and consumer demand for greener alternatives. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), EV sales grew by over 40% in 2022, further heightening competition among automotive giants.
Implications for Global Markets
The tariffs on Chinese EVs pose a significant challenge for many international automakers that rely on imports to meet domestic demand. In the United States, for example, various manufacturers have expressed concerns that increased tariffs could lead to higher prices for consumers. A recent study from the Canadian Automotive Partnership Council indicates that such tariffs could result in a price increase of up to $8,000 per vehicle, significantly slowing down adoption rates.
Moreover, European and North American companies have been prompted to reconsider their sourcing strategies and production locations, potentially leading to a fragmented supply chain. This situation could encourage further domestic production in regions like North America and Europe, mitigating the reliance on Asian-made vehicles and components.
Conclusion
The recent tariffs imposed on electric vehicles by China underscore a pivotal shift in the global automotive landscape. As countries strive towards achieving net-zero emissions, the strategic moves on tariffs can reshape industry dynamics, influence sourcing strategies, and ultimately affect the prices paid by consumers. Analysts predict that these developments could lead to increased regional manufacturing and a potential lift in domestic employment, although the immediate impact may cause turmoil in the global market. Stakeholders must remain vigilant, as changes in trade policies continue to unfold, shaping the future of electric mobility.