Recent Iceland Volcano Eruptions: Effects and Future Forecasts

Introduction
Iceland, known for its stunning landscapes and active geology, has been witnessing increased volcanic activity. Recent eruptions highlight the significance of understanding volcanic behavior, especially in a region rich in geothermal energy and tourism. The eruptions not only pose risks to local communities but also have broader implications for climate and air travel globally.
Recent Volcanic Activity
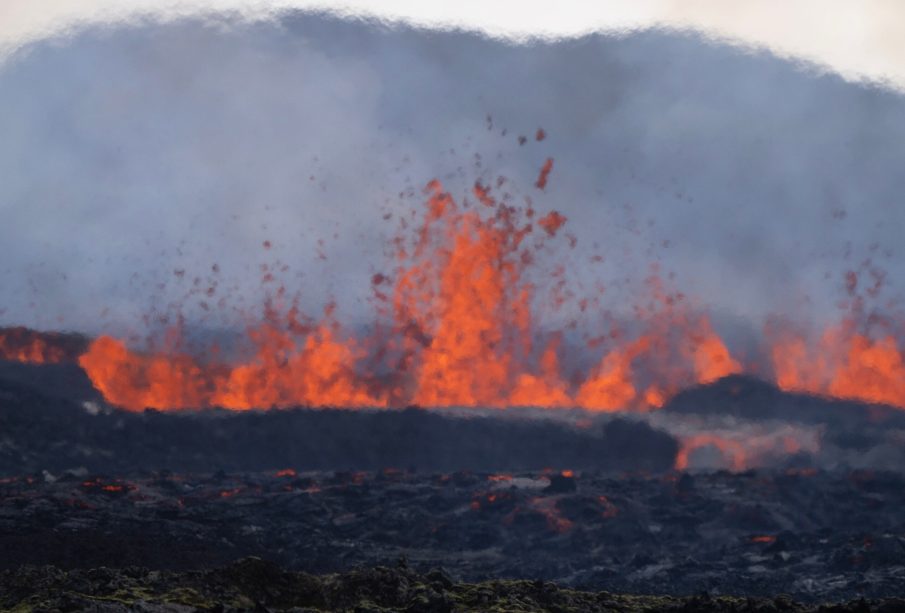
In late September 2023, the Fagradalsfjall volcano erupted, approximately 40 kilometers from Reykjavik. This marked the beginning of a notable series of eruptions, as recent geological studies revealed that the volcanic system is in a state of heightened unrest. Scientists have reported ongoing magma intrusions beneath the surface, indicating that additional eruptions could occur in the coming months.
The Icelandic Meteorological Office and other relevant authorities have been monitoring the situation closely, employing advanced technologies like drones and seismic networks to gather real-time data. The eruptions have produced significant lava flows and ash plumes, leading to temporary air quality issues and the closure of nearby roads. The ash cloud, while notable, has not yet severely impacted international air travel, which makes Iceland’s volcanic activity notable on a global scale.
Impact on Communities
The eruptions have caused concern among local residents, particularly those living near the volcanic zones. While there are evacuation plans in place, the authorities have assured that there are no immediate threats to populated areas. However, the Icelandic government emphasizes the importance of public awareness and preparedness in the face of such natural events.
Tourism is another aspect affected by volcanic eruptions. Iceland, which attracts millions of visitors each year, must balance the allure of its volcanic landscapes with the hazards that such natural phenomena present. According to the Icelandic Tourist Board, flight cancellations have seen a modest increase, but tourism operators remain optimistic about the resilience of the industry to adapt to these challenges.
Conclusion
Considering the recent volcanic eruptions in Iceland, experts forecast a continued period of volcanic activity, emphasizing the need for vigilance among residents and visitors alike. The eruptions serve as a reminder of the dynamic nature of Earth’s geological processes and their potential impact on society. As scientists work to enhance their understanding of Iceland’s volcanoes, communities are encouraged to remain informed and prepared for the potential challenges that may arise.