Norway vs New Zealand: A Comparative Overview

Introduction
Norway and New Zealand are two distinct countries located in different hemispheres, yet both are renowned for their stunning natural landscapes, high quality of life, and progressive social policies. Understanding the differences and similarities between these two nations is essential for travelers, students, and anyone interested in global cultures. This comparative analysis explores crucial aspects of both countries across diverse parameters.
Geography and Natural Landscapes
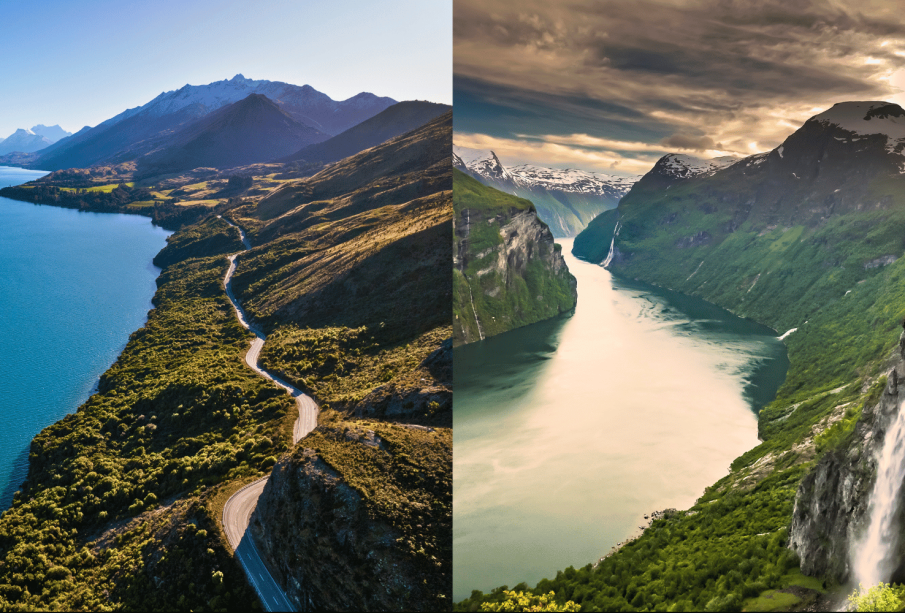
Norway is located in Northern Europe, known for its breathtaking fjords, coastal beauty, and rugged terrain. The country experiences a polar climate, characterized by long winters and short summers, which contributes to its stunning natural phenomena like the Northern Lights.
In contrast, New Zealand, situated in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, boasts a diverse topography that includes mountains, beaches, and lush rainforests. Its temperate climate embraces mild temperatures, making it ideal for outdoor activities year-round. Both nations prioritize environmental sustainability, with Norway investing heavily in green technologies and New Zealand implementing effective conservation practices.
Culture and Society
Both Norway and New Zealand have rich cultural heritages. Norway’s culture is heavily influenced by its Viking past, with traditions that celebrate art, music, and folklore. Festivals and community gatherings reflect the country’s deep-rooted customs. The official language is Norwegian, and the country maintains a welfare state that supports its citizens.
On the other hand, New Zealand is often recognized for its Maori heritage, which is integral to the country’s national identity. The Maori language, Te Reo, is an official language alongside English and New Zealand Sign Language. The society promotes inclusivity and celebrates cultural diversity, with numerous festivals highlighting both Maori and European traditions.
Economy and Development
Economically, Norway enjoys a robust economy fueled by its rich resources, including oil and gas. The country consistently ranks high in terms of GDP per capita and various quality-of-life indices. The government emphasizes renewable energy and sustainable practices, leading to an impressive environmental record.
New Zealand, while smaller in population, boasts a diverse economy relying on agriculture, tourism, and technology. The country’s commitment to innovation and support for small businesses fosters a dynamic entrepreneurial environment, contributing to steady economic growth.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Norway and New Zealand offer distinct yet commendable lifestyles defined by their unique geographies, cultures, and economic frameworks. While they differ in numerous ways, both nations serve as examples of societal progress and environmental consciousness. As global interest in sustainability and quality of life measures continues to rise, understanding the strengths of nations like Norway and New Zealand becomes increasingly significant. These insights may inspire policies and practices in other parts of the world, fostering a global dialogue on living harmoniously with nature and enhancing social equity.