Current Trends in Canada Bank Interest Rates
Introduction
The ongoing fluctuations in Canada bank interest rates have become a pivotal issue for consumers, businesses, and policymakers alike. With the economy still navigating through various challenges, understanding these rates is essential for making informed financial decisions. Interest rates not only affect mortgage payments, personal loans, and savings yields but also play a crucial role in shaping the overall economic landscape in Canada.
Current Interest Rate Trends
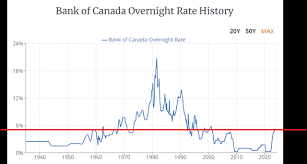
As of October 2023, the Bank of Canada (BoC) has maintained its key interest rate at 5.00%, a decision reflecting the central bank’s effort to manage inflation while encouraging economic growth. This rate, unchanged since July 2023, marks the highest level since 2001. The BoC’s stance comes amidst persistent inflationary pressures stemming from higher energy prices and supply chain disruptions.
According to data from Statistics Canada, inflation rates have eased slightly but remain above the Bank’s preferred target of 2%. In September, the consumer price index reported an annual increase of 3.5%, down from 4.1% in August. Economists predict that the central bank may adopt a cautious approach in the coming months, with potential future adjustments depending on the inflation trajectory and job market conditions.
Impact on Consumers and Businesses
The current interest rate environment significantly influences consumer behavior and business investments. Higher interest rates typically lead to increased borrowing costs, which can deter homebuyers and slow down real estate transactions. Mortgage applications have seen a decline, as potential buyers weigh the affordability of higher monthly payments.
In contrast, savers may benefit from enhanced interest rates on savings accounts and fixed deposits, encouraging financial prudence. However, businesses may face challenges in financing projects, leading to cautious spending on expansion and hiring.
Looking Ahead
Looking forward, Canada bank interest rates are expected to remain a focal point in economic discussions. Analysts suggest that if inflation continues to moderate, the BoC might consider rate cuts in 2024. Nevertheless, predictions remain cautious, as global economic uncertainties, especially in key trading partners like the United States, could influence domestic monetary policy decisions.
Conclusion
In summary, Canada bank interest rates are currently at a critical juncture, impacting various aspects of financial life across the nation. For consumers, understanding these changes is vital for making informed decisions on borrowing and saving. As the Bank of Canada navigates challenges in the economy, stakeholders should stay informed about potential future rate adjustments and their implications for personal and business finances.









