Australia’s Economic Recovery: A Look Ahead

Introduction
As the world slowly emerges from the repercussions of the COVID-19 pandemic, Australia stands as a noteworthy example of resilience and recovery. The country has made significant strides in rebuilding its economy, which is crucial not only for its citizens but also has implications for global economic stability. Understanding Australia’s recovery trajectory provides insight into potential outcomes for similar economies around the globe.
Current Economic Landscape
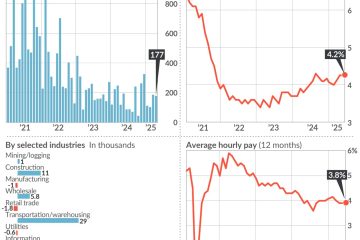
According to the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS), Australia’s economy grew by 3.1% during the first half of 2023. This growth has been primarily driven by strong consumer spending, robust exports, and a gradual rebound in the tourism sector. Additionally, the unemployment rate has dropped to its lowest level in over a decade, currently standing at 3.5%. This decrease is indicative of businesses reopening and hiring back workers who were previously laid off during the pandemic.
The Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) has also played a crucial role by maintaining low interest rates to encourage borrowing and investment. In June 2023, the RBA decided to hold the cash rate steady at 0.10%, emphasizing its commitment to supporting economic recovery until inflation rates return to target levels.
Challenges Ahead
Despite the apparent recovery, Australia faces several challenges. Supply chain disruptions continue to impact various industries, leading to shortages in materials and increased costs. Moreover, inflation has risen, threatening the purchasing power of consumers and the overall economic stability. In August 2023, the annual inflation rate reached 4.1%, a significant increase compared to the previous year.
The government is also grappling with the ongoing effects of climate change, which poses risks to agriculture and natural resources. Wildfires, flooding, and droughts could further complicate recovery efforts if not addressed proactively.
Conclusion
Australia’s path toward a full economic recovery remains promising yet challenging. As the nation continues to adapt to the post-pandemic world, its experiences may offer valuable lessons for other countries striving for recovery. Moving forward, maintaining a balance between stimulating growth and controlling inflation will be critical. For residents and stakeholders, actively engaging with these evolving economic conditions will be essential for ensuring continued progress, stability, and prosperity in Australia.