The Life and Legacy of John Henry Newman

Introduction
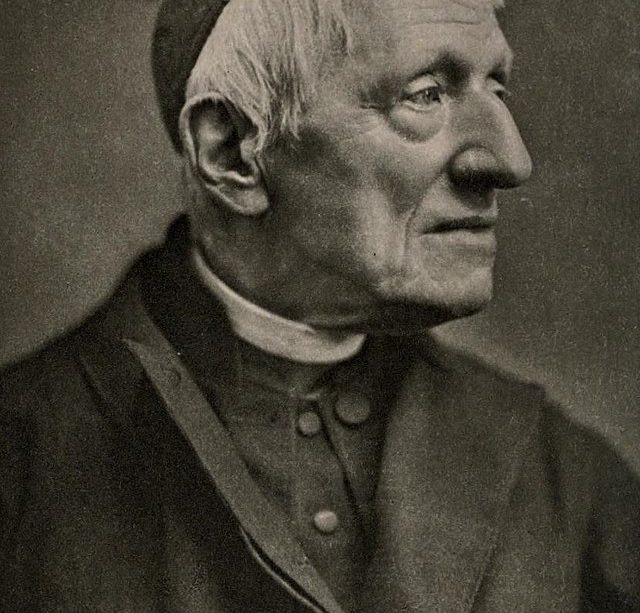
John Henry Newman, a pivotal 19th-century theologian and cardinal, has significantly influenced Christian thought and education worldwide. His journey from Anglicanism to Roman Catholicism, along with his theological works, provides profound insights into faith and reason. This article delves into Newman’s life, contributions, and ongoing relevance in today’s society.
Early Life and Conversion
Born on February 21, 1801, in London, Newman was educated at Oxford and became an influential figure in the Oxford Movement, which aimed to revive Catholic principles within the Anglican Church. His journey towards Catholicism began with his extensive theological inquiries and deepening understanding of the Church’s traditions. In 1845, Newman officially converted to Catholicism, a decision that sparked controversy and discussions about faith within the broader religious community.
Theological Contributions
Newman’s works, such as “Apologia Pro Vita Sua” and “The Idea of a University,” remain highly regarded. His thought emphasizes the relationship between faith and reason, challenging the notion of faith as mere sentiment. He argued for the importance of conscience and the development of doctrinal understanding, which has inspired generations of theologians, particularly within Catholic education. Newman’s philosophical approach encourages a responsible engagement with contemporary intellectual challenges.
Legacy in Education
Newman’s influence extends into educational philosophy, with his vision significantly shaping modern higher education. His idea of the university as a place for the pursuit of truth and the development of the whole person continues to resonate. Institutions, including the University of Newman in Canada, reflect his educational ideals, emphasizing a holistic approach that nurtures both intellect and character.
Canonization and Ongoing Relevance
In 2010, Pope Benedict XVI canonized Newman, recognizing his contributions to the Church and society. The canonization not only highlighted Newman’s relevance in historical context but also affirmed his role in addressing modern spiritual challenges. The themes in his writings, such as the importance of faith in a secular age, resonate with contemporary discussions regarding spirituality and moral philosophy.
Conclusion
John Henry Newman’s life and works continue to inspire dialogue about faith, education, and human experience. His emphasis on the interplay between reason and faith encourages a thoughtful approach to contemporary issues, making his legacy significant today. As society grapples with rapid change and moral questions, Newman’s insights into conscience and belief remain a guiding light for both individuals and communities. This enduring influence ensures that Newman’s thoughts and teachings will continue to provoke reflection and inspire subsequent generations.