Tesla’s New LFP Battery Factory in Nevada: A Game Changer
Introduction
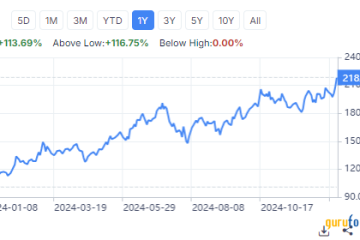
The establishment of Tesla’s LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate) battery factory in Nevada marks a significant milestone in the company’s efforts to lead the sustainable energy revolution. As electric vehicles gain popularity and battery technology advances, the demand for efficient, longer-lasting batteries becomes increasingly critical. Tesla’s new facility not only aims to meet this demand but also to stabilize the supply chain for these essential components, which could transform the automotive landscape and bolster the state’s economy.
Details of the Factory
Located in Storey County, Nevada, the Tesla LFP battery factory is part of the company’s broader strategy to produce affordable and sustainable battery solutions. Unlike traditional lithium-ion batteries, LFP batteries are known for their enhanced safety, stability, and lifecycle longevity. They are particularly well-suited for mass-market electric vehicles due to their lower costs and improved thermal stability. The factory is projected to significantly increase production capacity and, therefore, speed up the rollout of Tesla’s electric vehicles equipped with LFP technology.
The Nevada facility will focus on manufacturing battery cells specifically designed for Tesla’s energy products and vehicles. By establishing a local supply chain, Tesla aims to mitigate supply challenges experienced in the past, such as those related to battery material sourcing and logistics disruptions. Additionally, the factory is expected to create thousands of jobs, further enriching the local economy.
Environmental Impact and Future Prospects
One of the most significant advantages of LFP batteries is their reduced environmental impact compared to traditional batteries. LFP technology relies on abundant and non-toxic materials, which presents a more sustainable option for battery manufacturing. Tesla’s commitment to renewable energy and sustainability resonates with ongoing global efforts to combat climate change and reduce carbon footprints.
Looking ahead, the growth of the LFP battery market is anticipated to align with Tesla’s mission to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy. Experts suggest that as more manufacturers adopt LFP technology, the electric vehicle sector could see a reduction in costs, making EVs accessible to a broader demographic. Consequently, the success of Tesla’s Nevada factory could set a precedent for future battery production strategies across the industry.
Conclusion
The Tesla LFP battery factory in Nevada represents a crucial step towards more sustainable energy solutions and positions Tesla as a frontrunner in battery technology. With its potential to boost production capacity and foster local economic growth, the factory is likely to play a vital role in shaping the future of electric vehicles and battery sustainability. As the automotive industry continues to evolve, Tesla’s innovations may pave the way for a cleaner, greener future, setting an example for companies worldwide.