Measles: A Rising Concern for Public Health
The Importance of Understanding Measles
Measles, once considered eradicated in many developed nations, is making a troubling comeback. This viral infection, known for its high contagiousness, poses significant health risks not only to infected individuals but also to vulnerable populations like infants and those with compromised immune systems. Public health experts emphasize the importance of awareness and vaccination in combatting this disease, particularly in light of recent outbreaks across various regions.
Recent Outbreaks and Current Statistics
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), global measles cases rose by 79% in the first quarter of 2023 compared to the same period in 2022. As of October 2023, several provinces in Canada have reported increased numbers of measles cases, with Ontario and Quebec being particularly hard-hit. The Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC) confirmed 50 cases nationwide this year alone, a stark reminder of the virus’s resurgence amid declining vaccination rates.
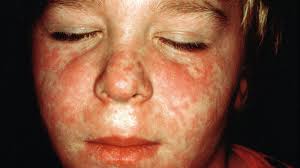
Symptoms and Transmission
Symptoms of measles typically appear seven to fourteen days after exposure, beginning with high fever, cough, runny nose, and inflamed eyes, followed by a characteristic rash. The virus is transmitted through respiratory droplets, making it highly contagious. An infected individual can spread the virus four days before the rash appears and up to four days after. The ease of transmission underscores the critical need for high vaccination coverage to create herd immunity, which protects those who cannot be vaccinated.
Vaccination as the Key to Prevention
The measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine is the primary line of defense against measles. The Canadian government recommends that children receive two doses of the MMR vaccine, starting at twelve months of age, followed by a second dose between four to six years. Despite the proven effectiveness of the MMR vaccine in preventing measles, vaccine hesitancy fueled by misinformation has contributed to a decline in immunization rates.
Health Authorities’ Response
In response to the rising cases, health authorities are ramping up vaccination campaigns and public health messaging to combat misinformation. Community outreach programs are being implemented to educate parents about the importance of vaccination and the safety of vaccines. Furthermore, health organizations are advocating for policy changes that ensure accessible vaccination services for all, particularly in underserved communities.
Conclusion: The Path Forward
The resurgence of measles is a stark reminder of the ongoing challenges in public health, particularly the need for robust vaccination programs. As communities face rising cases, it is crucial for individuals to be informed about the risks associated with measles and the benefits of vaccination. Continued public health efforts and community involvement will be essential in preventing future outbreaks and ensuring the safety and health of future generations.




