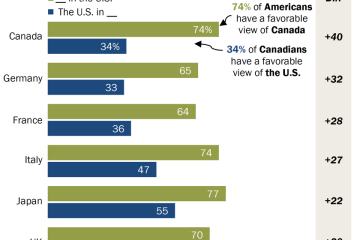
Recent Developments in the Ivory Coast

Introduction
The Ivory Coast, officially known as Côte d’Ivoire, is an essential nation in West Africa, recognized for its vibrant economy and political significance. As the world’s largest producer of cocoa beans, its stability is crucial not just for its citizens but for global markets reliant on this commodity. Ongoing developments in governance, economy, and international relations make the Ivory Coast a prominent topic of discussion.
Economic Landscape
As of 2023, the Ivory Coast has experienced robust economic growth, boasting a Gross Domestic Product (GDP) increase of approximately 6.5% over the past year. This growth is largely driven by its agricultural exports, particularly cocoa, cashew nuts, and palm oil, which together account for a significant portion of the country’s earnings. The Ivorian government has also focused on diversifying its economy, encouraging investments in infrastructure and technology.
Recent reports from the World Bank highlight the government’s initiatives to improve agricultural productivity through sustainability and innovation. For instance, investments in modern farming techniques have increased cocoa production efficiency and quality, vital for maintaining its global market share. Additionally, the government’s commitment to enhancing education and training in agricultural practices stems from a need to adapt to climate change, ensuring long-term agricultural resilience.
Political Stability and Governance
Politically, the Ivory Coast has made significant strides towards stability following years of civil conflict that peaked in 2010-2011. The current administration, led by President Alassane Ouattara, has prioritized national reconciliation and democratic governance. However, the recent presidential elections in late 2020 raised concerns about political tensions and the potential for unrest, leading to ongoing debates around electoral reforms and participation of opposition parties.
In 2023, the government has worked to foster transparency, with efforts to engage various political factions in dialogue. International observers have noted improvements, but the success of these initiatives remains critical as the country approaches legislative elections in 2025. The focus on sustainable political practices will be crucial in maintaining the momentum for growth and stability.
Conclusion
The Ivory Coast stands at a crossroads where economic growth and political stability are both essential for future progress. The country’s capacity to effectively manage its agricultural sector and political landscape will determine its trajectory in the coming years. For Ivorian citizens and international stakeholders alike, the stability of the Ivory Coast remains a significant concern, influencing not only regional dynamics but also global markets reliant on its rich agricultural output. As the world watches, the Ivory Coast’s path forward is of paramount importance, pointing toward resilience in the face of challenges.