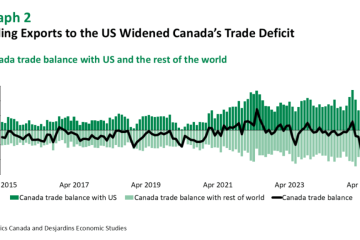
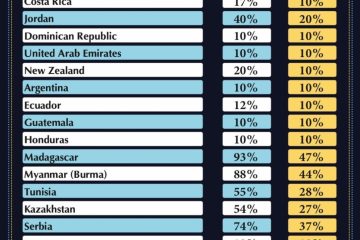
Understanding Fannie Mae and Its Impact on Housing Finance

Introduction
Fannie Mae, officially known as the Federal National Mortgage Association, plays a crucial role in the United States housing finance system. As a government-sponsored enterprise (GSE), it was established to facilitate liquidity in the mortgage market, making homeownership accessible to a more extensive range of Americans. Understanding the operations and recent changes within Fannie Mae is significant, particularly as it adapts to evolving economic conditions and housing policies.
Recent Developments
In recent months, Fannie Mae has faced several challenges and opportunities that could reshape the housing landscape. As of August 2023, the agency reported a net income of $3.6 billion for the second quarter, a notable increase compared to previous quarters, signaling a recovery from the market disruptions caused by the pandemic. This performance is attributed to rising home values and a refocus on mortgage servicing that has improved profitability.
Moreover, Fannie Mae, alongside other GSEs, continues to implement new guidelines aimed at promoting affordable housing initiatives. Recent announcements have highlighted efforts to streamline the mortgage underwriting process, which is expected to facilitate access for underserved communities. This initiative, part of Fannie Mae’s broader mission to enhance equitable homeownership, seeks to address the existing homeownership gaps in minority communities.
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, Fannie Mae is poised to embrace further changes driven by market demands and housing policies. The Federal Housing Finance Agency (FHFA), which oversees Fannie Mae, has proposed new capital requirements that may impact its operating model. While these changes aim to bolster the resilience of the housing finance system, they may also lead to higher mortgage costs for consumers in the market.
Additionally, interest rates continue to fluctuate, and with the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy tightly interlinked with economic recovery, the potential effects on housing demand and refinancing cannot be overlooked. Fannie Mae’s ability to navigate these challenges will be pivotal in maintaining stability in the housing market as the economy evolves.
Conclusion
Fannie Mae remains a key player in the housing finance sector, with its actions impacting millions seeking homeownership across the U.S. As it adapts to shifting economic conditions and regulatory landscapes, its influence on mortgage availability for American families will continue to be significant. Stakeholders should closely monitor these developments to understand their potential implications for the housing market and broader economy. Overall, Fannie Mae’s commitment to facilitating homeownership is vital, and its future initiatives will be critical in shaping equitable access to housing.