Understanding Canada’s Core Inflation Rate in 2023
Introduction
The core inflation rate in Canada is a crucial economic indicator that reflects the underlying trends in the price level, excluding volatile items such as energy and food. Understanding this metric is essential for policymakers, economists, and consumers alike, as it plays a significant role in monetary policy decisions made by the Bank of Canada. As of October 2023, this measure is garnering attention due to its implications for inflation control and economic stability.
Current Trends in Core Inflation
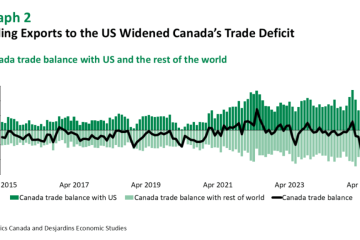
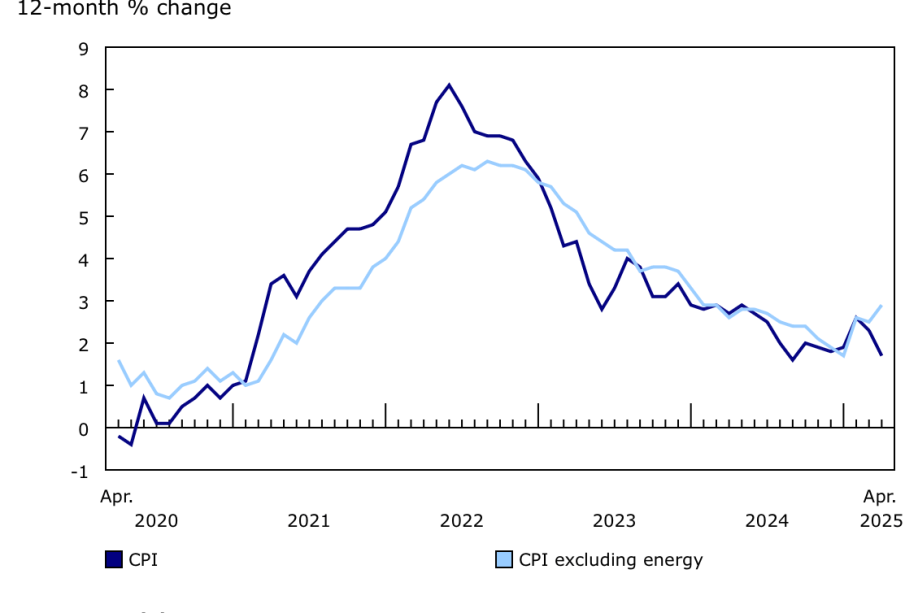
According to the latest data released by Statistics Canada, the core inflation rate for September 2023 has remained stable at around 3.5%, slightly higher than the central bank’s target of 2%. This stability occurs despite fluctuations in the headline inflation rate, which has been influenced by rising energy prices and supply chain disruptions. Notably, while categories that directly impact consumers, such as transportation and housing, have seen price increases, core inflation signals that underlying inflation is moderating.
Factors Influencing Core Inflation
Several factors contribute to the current state of core inflation in Canada. First, wage growth has been observed across various sectors, impacting consumer prices as companies adjust their pricing strategies to account for increased salary expenses. Furthermore, persistent global supply chain issues, exacerbated by ongoing geopolitical tensions, continue to affect the availability and pricing of goods. In July 2023, the Bank of Canada raised interest rates to 5% in an effort to cool inflation, and the effects of this policy are being closely monitored.
Potential Economic Impacts
The implications of current core inflation trends are far-reaching. Sustained rates above the target can lead to increased borrowing costs, affecting both consumers and businesses. As interest rates rise, investment may slow down, which can hamper economic growth. Conversely, if inflation eases due to policy measures and external factors stabilize, the economy may experience a rebound, leading to improved consumer spending and confidence.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the core inflation rate is an essential barometer for assessing the health of the Canadian economy. Understanding its current trends, influences, and potential impacts is crucial for stakeholders making informed decisions. As the Bank of Canada continues to navigate the complexities of economic recovery, monitoring core inflation will be vital for anticipating future monetary policy moves. With numerous factors at play, including policy adjustments and global economic conditions, careful attention to this indicator will be necessary for Canadians moving forward.