The Importance of China’s Rare Earth Minerals in Today’s Economy
Introduction
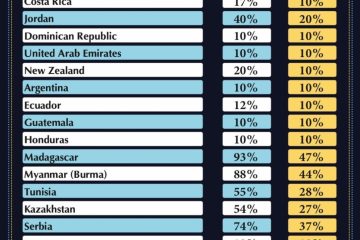
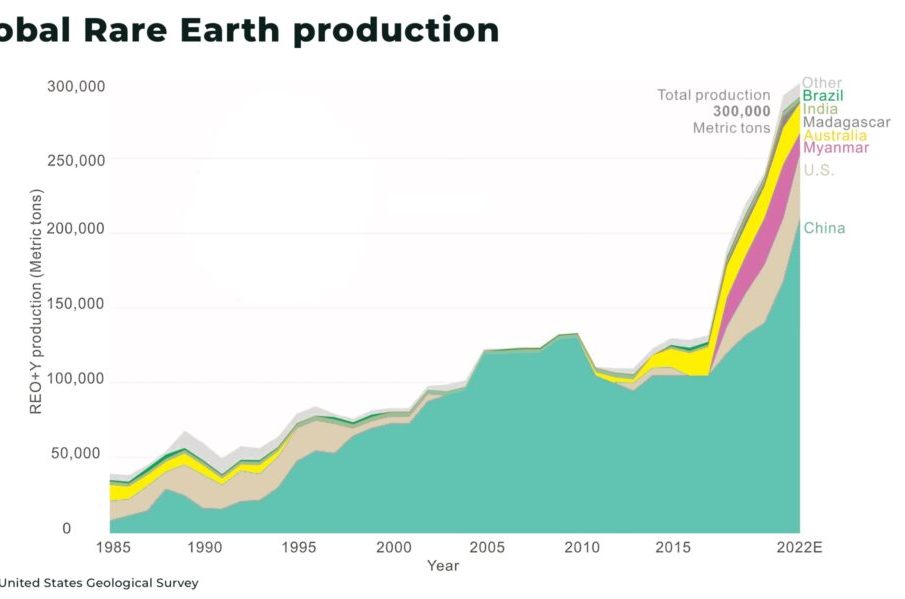
Rare earth minerals, a group of 17 elements essential for various high-tech applications, have become a focal point in global trade and technology development. China dominates the rare earth market, supplying over 60% of the world’s needs. Understanding China’s role in this sector is crucial as these minerals are pivotal in manufacturing everything from smartphones to electric vehicles. The competition for these resources is intensifying as technological advancements accelerate, making this topic highly relevant in today’s geopolitical landscape.
China’s Dominance in Rare Earth Minerals
China’s control over the rare earth supply chain has been a significant aspect of its economic strategy. The country possesses nearly 40% of the world’s known rare earth reserves and controls a substantial portion of the extraction and processing capabilities. This dominance is not only economic but also strategic, as rare earths are vital for defense technologies, telecommunications, and renewable energy advancements.
Recent reports indicate that China has ramped up its production of rare earth minerals, responding to increasing global demand, particularly from Western nations striving for independence in critical supply chains. In addition to existing extraction, China is investing heavily in mining technology and infrastructure to enhance its production efficiency.
Global Implications
China’s rare earth supply is critical for many industries and its geopolitical stance has significant implications. Tensions between the U.S. and China have raised concerns about supply disruptions. In 2021, China briefly halted exports of rare earths to Japan in a bid to exert influence, demonstrating how quickly rare earth trade can become an instrument of geopolitical power.
In response to these concerns, nations like the United States and Australia are investing in their rare earth mining capabilities to reduce dependence on China. Legislative efforts, such as the United States’ Rare Earths Supply Chain Technology and Resource Transformation Act, aim to establish domestic sources of these critical minerals, fostering a more resilient supply chain.
Conclusion
The importance of China’s rare earth minerals cannot be overstated. As technology continues to evolve and the demand for clean energy solutions grows, the global stakes surrounding rare earth elements will likely increase. Countries are reevaluating their strategies to ensure a stable supply of these crucial resources, which will shape the course of international relations and economic policies in the coming years. For readers, understanding this dynamic landscape is essential, as it affects everything from technology costs to environmental sustainability efforts around the world.