Understanding the Importance of Premarket Trading
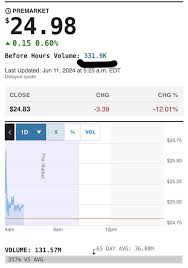
Introduction
Premarket trading is a critical component of the financial markets, providing investors with an early glimpse into how the markets may perform on a given day. This trading period occurs before the official market opening, allowing traders to react to news and events that could influence stock prices. Understanding premarket trading is essential for investors looking to make informed decisions and capitalize on potential market movements.
The Mechanics of Premarket Trading
Premarket trading typically takes place between 4:00 AM and 9:30 AM EST, with platforms like E*TRADE and TD Ameritrade facilitating these transactions. During this time, stocks can be traded outside of the normal trading hours, which helps to create price discovery and allows traders to position themselves ahead of the market’s official open. High volatility and lower liquidity often characterize premarket sessions, leading to price swings that may not reflect the broader market’s rhythm.
Recent Developments in Premarket Trading
Recently, premarket trading has garnered more attention due to its role in reflecting investor sentiment prior to major market openings. For instance, in anticipation of the Federal Reserve’s interest rate decisions, stocks often exhibit significant movements in premarket hours. Reports indicate that stocks like Tesla and Apple frequently see heightened trading activity as investors react to earnings reports or market news released before the opening bell.
As of late October 2023, significant premarket movements have been noted in technology stocks, driven by advancements in AI and concerns over inflation. For example, shares of several tech companies rose sharply after positive earnings forecasts were made public prior to market openings. Conversely, negative news such as regulatory changes or economic data releases has led to sharp declines in premarket trading.
Investment Strategies Involving Premarket Trading
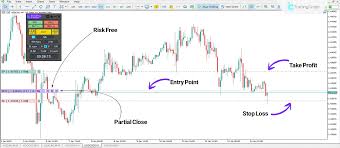
Traders and investors often use premarket trading data to inform their strategies. For short-term traders, this period can present opportunities to react quickly to news and capitalize on price discrepancies. Long-term investors may also pay attention to premarket activity but typically focus on the broader trends rather than intraday fluctuations.
Conclusion
The significance of premarket trading cannot be overstated. As a crucial barometer of market sentiment, it provides valuable insights into potential price movements and investor trends. As markets continue to evolve and investor strategies become more sophisticated, understanding premarket trading will remain essential for both new and experienced investors alike. Staying informed and reacting to premarket developments could be the difference between profiting or enduring losses in today’s fast-paced market environment.