Asteroid 2024 YR4: A New Near-Earth Object of Interest
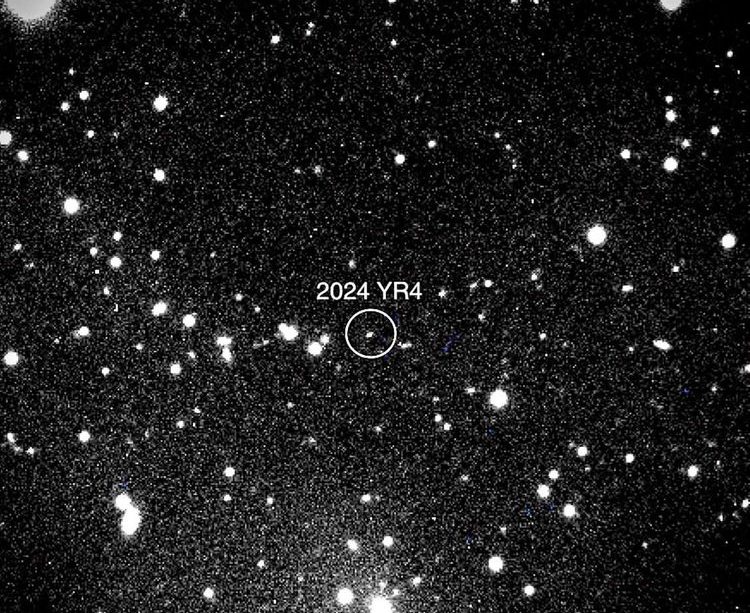

Introduction to Asteroid 2024 YR4
In recent months, the discovery of Asteroid 2024 YR4 has sparked interest among astronomers and space enthusiasts alike. This near-Earth object (NEO) is categorized under the Apollo group of asteroids, which are known for their orbits that bring them close to Earth. Understanding such asteroids is vital as they can pose potential threats to our planet, yet they also present opportunities for scientific exploration and research.
Discovery and Characteristics
Asteroid 2024 YR4 was detected on January 6, 2024, by the Pan-STARRS observatory in Hawaii, which is renowned for its efforts in tracking NEOs. Measuring approximately 120 meters in diameter, this asteroid is relatively small compared to many others, but it is large enough to be significant in terms of space impact studies. Its orbit brings it into proximity with Earth every few years, creating a unique opportunity for observation.
Close Approach Details
Asteroid 2024 YR4 is expected to make its closest approach to Earth on April 15, 2024, when it will pass within 0.03 astronomical units (about 4.5 million kilometers or 2.8 million miles) of our planet. To put this distance into perspective, that is about 11 times farther away than the Moon. Despite this safe distance, astronomers are eager to study the asteroid during its flyby, as observations can provide insights into its composition, structure, and potential trajectory in the future.
Potential Impact and Mitigation Efforts
While 2024 YR4 is currently classified as a non-threatening asteroid, ongoing monitoring is essential. The Near-Earth Object Program, managed by NASA, continuously tracks and evaluates NEOs to assess their potential threat levels. If any future assessments indicate a risk of impact, various strategies, including deflection missions, may be considered to safeguard Earth from any threats posed by similar asteroids.
Conclusion
The discovery of Asteroid 2024 YR4 serves as a reminder of the dynamic and ever-changing nature of our solar system. Its upcoming close approach offers a valuable chance for scientists to gather data that can enhance our understanding of asteroids and their behavior. As ongoing advancements in technology improve our ability to detect and study these celestial bodies, we gain greater insight into both potential hazards and the origins of the solar system.