The Impact of Chinese Tariffs on Canada’s Economy
Introduction: Understanding Chinese Tariffs
Chinese tariffs have become a crucial topic for Canadian businesses and policymakers, especially in the wake of evolving trade relationships. These tariffs not only affect the direct import and export of goods but also influence global supply chains, inflation, and the overall economy in Canada.
Current Situation
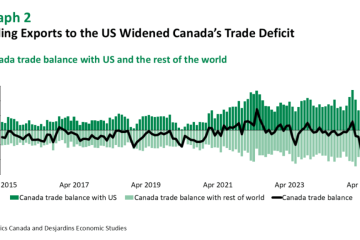
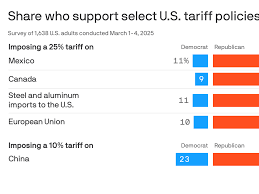
As of 2023, China has implemented various tariffs on goods imported from Canada as part of its broader trade strategy, which aims to cushion domestic industries against foreign competition. The Canadian government reported a 15% increase in the tariffs on several agricultural products, including canola and pork, which are among Canada’s key exports. This increase in tariffs poses significant challenges for Canadian farmers and exporters, who are struggling to maintain competitive prices.
Effects on Canadian Markets
The rise of tariffs has shown several repercussions in Canada’s economy. Businesses affected by these tariffs have started to report reduced profit margins, and many are re-evaluating their supply chains to adapt to the changing landscape. A report from the Canadian Institute for International Trade highlighted that approximately 30% of surveyed Canadian exporters have faced declining revenues due to Chinese tariffs.
Moreover, this situation has contributed to rising consumer prices as companies look to offset the additional costs imposed by tariffs. Economists warn that long-term trade disputes can lead to product shortages and inflation, creating a challenging environment for consumers.
Government Response and Future Outlook
In response to these challenges, the Canadian government is exploring several avenues to mitigate the impact of tariffs. Diplomatic efforts are underway to negotiate better trade terms with China and to advocate for the reduction or removal of these tariffs. Additionally, Canada is looking to diversify its export markets to reduce dependency on the Chinese market, targeting regions such as Southeast Asia and Europe.
Forecasts suggest that if the trade tensions persist, Canada might have to adapt further by increasing investments in innovation and local production to buffer its economy against external shocks.
Conclusion: The Importance of Adaptation
In conclusion, the implications of Chinese tariffs on Canada’s economy are profound and multifaceted. They underscore the need for Canadian businesses to remain agile and for the government to pursue strategic international partnerships while fostering resilience in the domestic market. Staying informed and prepared for potential changes in the trade environment will be essential for navigating these turbulent economic waters.