Understanding Reciprocal Tariffs and Their Impact on Trade
Introduction to Reciprocal Tariffs
Reciprocal tariffs are an essential aspect of international trade policy, impacting economic relationships among countries. These tariffs are implemented by one country to mirror the tariff policies of another, often aiming to promote fair trade and protect domestic industries. As nations grapple with post-pandemic economic recovery and shifting geopolitical dynamics, understanding reciprocal tariffs has become increasingly relevant for businesses, policymakers, and consumers alike.
The Evolution of Reciprocal Tariffs
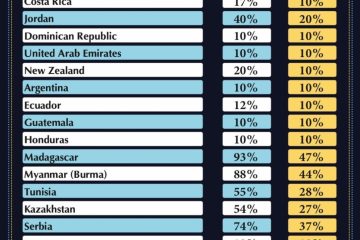
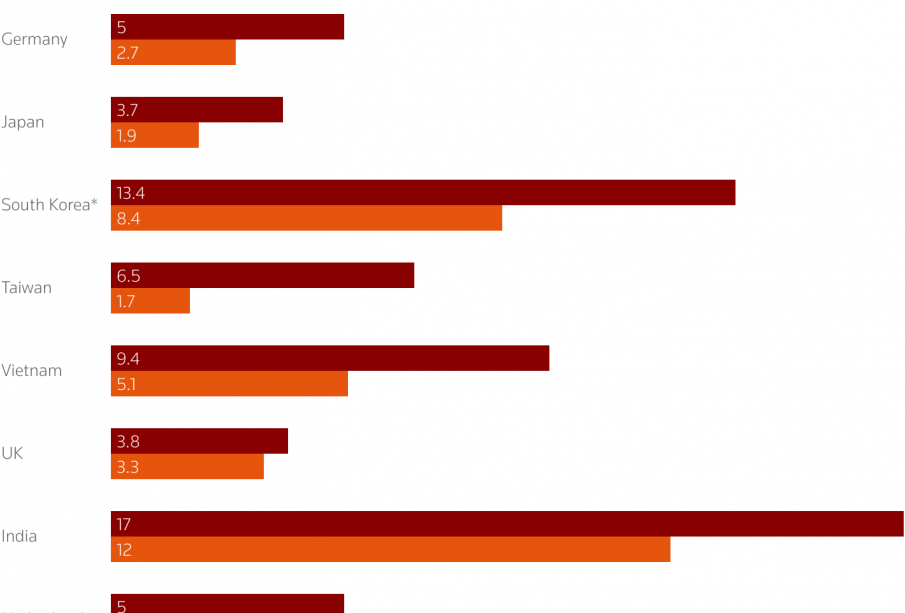
Historically, countries have utilized tariffs as a tool for negotiation in trade agreements. The concept of reciprocal tariffs gained prominence as nations sought to establish balanced trade relationships. For instance, the United States and China have engaged in reciprocal tariffs, raising costs on various imports to protect their respective markets. Recent data shows that tariffs between these two economic powerhouses have escalated, impacting nearly $600 billion in goods since 2018.
Current Events Surrounding Reciprocal Tariffs
Recent discussions at the World Trade Organization (WTO) highlight the urgency of addressing the ongoing trade tensions exacerbated by reciprocal tariffs. As countries face inflationary pressures and supply chain disruptions, policymakers are increasingly called upon to find solutions that minimize the economic burden on consumers while ensuring fair competition for local industries. In late 2023, Canada signaled a potential recalibration of its tariff policies to facilitate smoother trade relations with both the United States and Europe, indicating a shift in focus towards collaboration rather than confrontation.
Implications for Global Trade
The implications of reciprocal tariffs extend beyond mere economic statistics; they can have profound effects on global supply chains, consumer prices, and employment rates. As tariffs increase, businesses may face higher operational costs, which often translate into increased prices for consumers. Furthermore, industries reliant on international trade may find themselves at a competitive disadvantage if tariffs are not harmonized across key markets. Consequently, there are growing calls for a multilateral approach to trade, wherein countries work collaboratively to reduce or eliminate tariffs, thereby promoting a more stable and equitable trading environment.
Conclusion and Future Outlook
In conclusion, reciprocal tariffs represent a complex yet crucial element of international trade relations. As the global economy continues to evolve, the need for coherent tariff policies that prioritize fair competition and economic growth is more significant than ever. Businesses and consumers alike should stay informed about changes in tariff policies to better navigate the implications for their markets. Looking ahead, it is essential for countries to pursue diplomatic avenues to manage and potentially dismantle reciprocal tariff barriers, fostering a more inclusive and prosperous global economy.